Introduction: The Foundation of Village Progress
When we talk about the bedrock of Indian democracy and the engine of grassroots development, the role of the Gram Panchayat and its elected head, the Sarpanch, comes to the forefront. Understanding the multifaceted Sarpanch Responsibilities is not just an academic exercise; it’s essential for every rural resident in Sangli district to grasp how their village functions, progresses, and addresses its challenges. The Sarpanch is more than just a figurehead; they are the chief executive, the primary administrator, and the most accessible leader for the millions living in India’s villages.
This comprehensive article will meticulously outline the array of duties and powers vested in a Sarpanch, delving into how their actions directly influence public services, infrastructure, social welfare, and economic upliftment within the villages of Sangli. From managing local finances to implementing government schemes, the Sarpanch’s role is pivotal in shaping the present and future of rural Maharashtra.
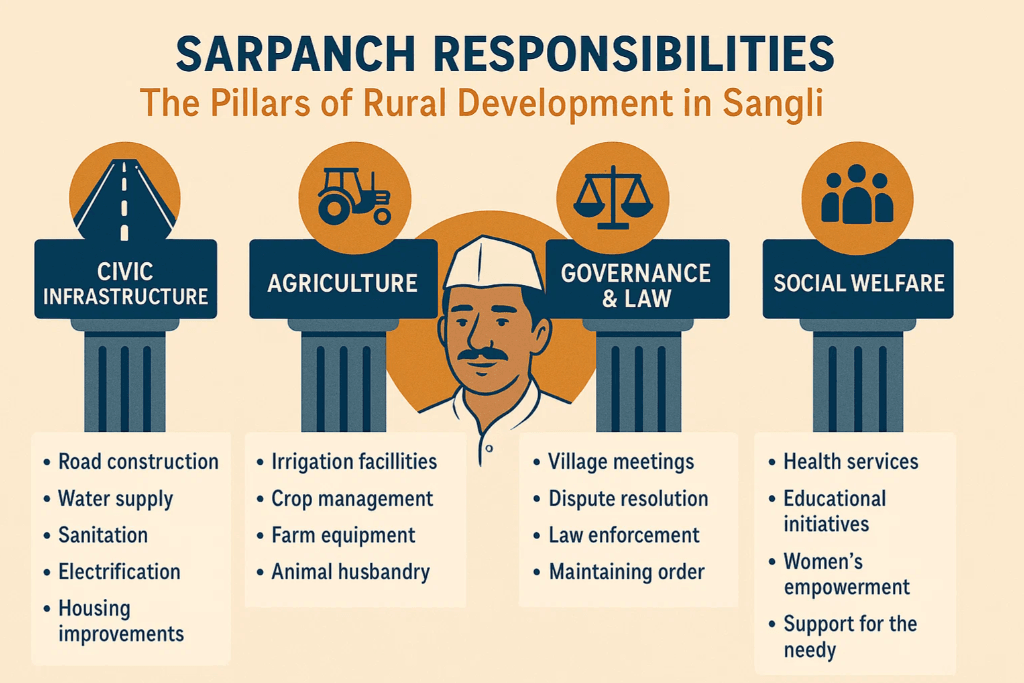
I. The Constitutional Mandate: Why Sarpanch Responsibilities are Crucial
The concept of Panchayati Raj, India’s system of local self-governance in rural areas, received a significant boost with the 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act of 1992. This landmark amendment provided constitutional status to Gram Panchayats, making them the third tier of governance, below the Union and State governments. The aim was simple yet profound: to decentralize power and empower local communities to manage their own affairs, fostering true ‘Gram Swaraj’ (village self-rule) as envisioned by Mahatma Gandhi.
At the heart of this decentralized system lies the Gram Panchayat, and at its helm, the Sarpanch. Elected directly by the members of the Gram Sabha (the body comprising all adult voters in the village), the Sarpanch serves as the chairperson of the Gram Panchayat. They are the link between the village population and the higher administrative tiers, responsible for translating local needs into actionable plans and ensuring their execution. The effectiveness of rural development in Sangli, as in any other district, heavily relies on the diligent and responsible discharge of Sarpanch Responsibilities.
II. Core Administrative and Executive Sarpanch Responsibilities
The Sarpanch acts as the executive head of the Gram Panchayat. Their administrative and executive duties form the backbone of village governance.
- Presiding Over Meetings: The Sarpanch chairs the meetings of the Gram Panchayat. These meetings are crucial for discussing village issues, planning development activities, and passing resolutions. The Sarpanch ensures that discussions are orderly and that decisions are made democratically.
- Implementing Resolutions: Once resolutions are passed by the Gram Panchayat, it is a primary Sarpanch responsibility to ensure their effective implementation. This involves coordinating with various government departments, securing necessary approvals, and overseeing project execution.
- Financial Management: This is one of the most critical Sarpanch Responsibilities. They are custodians of the Gram Panchayat’s funds. This includes:
- Revenue Collection: Ensuring the timely collection of local taxes (like property tax, water tax), fees, and levies imposed by the Gram Panchayat.
- Fund Utilization: Managing grants received from state and central governments for various development schemes (e.g., Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act – MGNREGA, Swachh Bharat Mission).
- Budgeting: Preparing and presenting the annual budget of the Gram Panchayat for approval.
- Maintaining Accounts: Ensuring proper maintenance of all financial records, accounts, and registers, and ensuring transparency in financial transactions.
- Supervision of Staff: The Sarpanch supervises the work of the Gram Sevak (Village Secretary) and other Gram Panchayat staff, ensuring that administrative tasks are carried out efficiently.
- Maintaining Records: Ensuring accurate and up-to-date records of births, deaths, marriages, and other vital statistics within the village. This data is crucial for various planning and social welfare programs.
- Public Relations and Communication: Acting as the official spokesperson for the Gram Panchayat, communicating decisions, policies, and development plans to the villagers. They also serve as the first point of contact for external agencies and government officials.
- Dispute Resolution: Often, the Sarpanch acts as a mediator in minor local disputes, promoting harmony and resolving conflicts within the village community. While not a formal judicial role, this informal responsibility is vital for social cohesion.
III. Development-Oriented Sarpanch Responsibilities
Beyond administration, the Sarpanch is a key driver of development in their village. Their responsibilities here are directly linked to improving the quality of life for their constituents.
- Infrastructure Development: This forms a significant portion of Sarpanch Responsibilities. It includes:
- Roads and Connectivity: Ensuring the construction and maintenance of internal village roads, approach roads, and culverts, crucial for connecting villagers to markets, schools, and health centres.
- Water Supply: Managing and ensuring adequate and safe drinking water supply, including the maintenance of village wells, borewells, and piped water schemes.
- Sanitation and Drainage: Overseeing the construction and maintenance of village drains, public toilets, and promoting household sanitation.
- Street Lighting: Providing and maintaining street lights to ensure safety and convenience, especially during night hours.
- Community Assets: Development and maintenance of public spaces like community halls, playgrounds, and cremation grounds.
- Public Health and Hygiene:
- Promoting cleanliness drives and waste management initiatives (e.g., solid and liquid waste management projects under Swachh Bharat Mission).
- Liaising with Primary Health Centres (PHCs) and Sub-Centres to ensure the availability of basic healthcare services and medicines.
- Organizing health awareness campaigns on topics like sanitation, nutrition, family planning, and disease prevention (e.g., dengue, malaria campaigns, which are crucial in districts like Sangli).
- Taking preventive measures during epidemics or natural calamities.
- Education and Literacy:
- Promoting primary education and ensuring maximum enrollment in village schools.
- Monitoring the functioning of Anganwadis and primary schools within the village.
- Advocating for better educational facilities, infrastructure, and teaching quality.
- Working towards achieving full literacy in the village.
- Agriculture and Allied Activities:
- Facilitating the implementation of agricultural schemes and providing information to farmers about modern farming techniques, new seeds, and government subsidies.
- Promoting water conservation methods for agriculture, especially vital in regions dependent on monsoon.
- Encouraging animal husbandry, fisheries, and other allied activities to diversify rural livelihoods.
- Social Welfare and Poverty Alleviation:
- Identifying eligible beneficiaries for various central and state government welfare schemes (e.g., old-age pensions, widow pensions, housing schemes like Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Gramin).
- Ensuring the welfare of vulnerable sections of society, including Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Other Backward Classes, women, children, and persons with disabilities.
- Promoting self-help groups (SHGs) for women’s empowerment and economic independence.
- Implementing schemes like MGNREGA to provide guaranteed employment opportunities to rural households.
- Environmental Protection:
- Promoting tree plantation drives and maintaining village green spaces.
- Working towards sustainable use of natural resources.
- Raising awareness about climate change and local environmental issues.
- Ensuring compliance with environmental regulations at the local level.
IV. The Sarpanch and the Gram Sabha: A Symbiotic Relationship
Central to the discharge of Sarpanch Responsibilities is their relationship with the Gram Sabha. The Gram Sabha is the general body of all adult voters registered in the electoral rolls of a village. It is the most powerful body at the grassroots level, acting as the ‘village parliament’.
- Accountability: The Sarpanch and other Gram Panchayat members are accountable to the Gram Sabha. All major decisions regarding village development plans, budgets, and scheme beneficiaries must be presented and approved by the Gram Sabha.
- Transparency: The Gram Sabha provides a platform for transparency, where villagers can question expenditures, demand information, and hold their elected representatives responsible.
- Participation: Active participation of villagers in Gram Sabha meetings is crucial for effective governance. It allows citizens to voice their opinions, propose development works, and provide valuable feedback.
- Mandate: The resolutions passed by the Gram Sabha are binding on the Gram Panchayat. The Sarpanch’s executive power is largely derived from and exercised in accordance with the will of the Gram Sabha.
Without a strong and engaged Gram Sabha, the Sarpanch Responsibilities can become merely administrative, losing their democratic spirit and community connection. The Sarpanch is expected to facilitate and encourage active participation in Gram Sabha meetings.
V. Challenges in Fulfilling Sarpanch Responsibilities
Despite the extensive list of duties, Sarpanches often face significant hurdles in fulfilling their roles effectively. Understanding these challenges provides context for their work and highlights areas where citizen support can be crucial.
- Limited Financial Autonomy: While Gram Panchayats receive grants, their own revenue-generating capacity is often limited. They frequently depend on funds from state and central governments, which can lead to delays and influence.
- Bureaucratic Red Tape: Navigating the complex administrative hierarchy, getting sanctions from block and district level officials, and dealing with delays can be a major challenge.
- Lack of Training and Capacity Building: Many Sarpanches, especially those newly elected, may not have formal training in public administration, financial management, or legal frameworks, which are vital for effective governance. Training programs are essential to bridge this gap.
- Political Interference and Factionalism: Village politics can sometimes be intense, leading to factionalism that hampers consensus-building and development work. Political interference from higher-level politicians can also undermine the autonomy of the Gram Panchayat.
- Inadequate Support Staff: Gram Panchayats often operate with limited staff (e.g., a single Gram Sevak serving multiple villages), which can strain administrative capacity.
- Lack of Awareness Among Citizens: If villagers are unaware of the Gram Panchayat’s functions and their own rights, they may not participate actively in Gram Sabhas or hold their representatives accountable, leading to a passive citizenry.
- Infrastructure Deficiencies: In many remote villages of Sangli, basic infrastructure like reliable electricity, internet connectivity, and proper transport links can be a challenge, affecting communication and project implementation.
- Natural Disasters: Being directly on the ground, Sarpanches are often the first responders during natural calamities like floods (common in parts of Sangli due to the Krishna River) or droughts, demanding immediate and effective disaster management.
- Accountability and Transparency Issues: Despite frameworks, ensuring complete transparency in public works and financial dealings at the local level can sometimes be challenging, requiring vigilance from citizens and oversight bodies.
VI. The Sarpanch’s Role in Specific Schemes (Illustrative for Sangli)
The effectiveness of Sarpanch Responsibilities is often seen in the implementation of specific government schemes designed for rural upliftment. Let’s look at a few relevant to Sangli:
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA):
- The Sarpanch, along with the Gram Sevak, is instrumental in identifying eligible households, preparing job cards, sanctioning work, and ensuring timely wage payments.
- They play a key role in identifying local works (e.g., farm ponds, check dams, road construction) that can be undertaken under MGNREGA, providing both employment and community assets.
- This scheme is crucial for providing a safety net for rural labour, particularly in agricultural districts like Sangli during lean seasons.
- Swachh Bharat Mission (Grameen – SBM-G):
- Sarpanch Responsibilities include driving the mission to make the village Open Defecation Free (ODF) and sustaining that status.
- They oversee the construction of individual household latrines (IHHLs) and community sanitary complexes.
- Crucially, they lead solid and liquid waste management (SLWM) initiatives, promoting composting, segregation of waste, and community-level waste disposal systems. This is vital for public health in Sangli’s villages.
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Gramin (PMAY-G):
- The Sarpanch plays a role in identifying eligible beneficiaries for affordable housing, ensuring that houses are built according to guidelines, and assisting beneficiaries in accessing financial aid.
- This directly impacts the living conditions of the rural poor.
- Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM):
- This mission aims to provide tap water connection to every rural household. The Sarpanch leads the Village Water and Sanitation Committee (VWSC) and oversees the planning, implementation, and maintenance of village water supply infrastructure.
- For a district like Sangli, ensuring sustainable and safe drinking water sources is a key public health priority.
- National Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM) / Maharashtra State Rural Livelihoods Mission (MSRLM):
- Sarpanches encourage the formation of Self-Help Groups (SHGs), especially for women, and facilitate their access to credit and market linkages.
- This directly contributes to economic empowerment and poverty reduction at the village level.
By actively participating in these schemes, the Sarpanch moves beyond basic administration to become a facilitator of significant social and economic transformation in their village.
VII. Engaging with Your Sarpanch: Empowering Rural Sangli
Just as it’s important to understand Sarpanch Responsibilities, it’s equally vital for citizens to know how to effectively engage with them. Active citizen participation strengthens local governance and ensures accountability.
- Attend Gram Sabha Meetings: This is the single most powerful tool. Attend regularly, voice your concerns, ask questions about budgets and schemes, and participate in decision-making. Your vote in the Gram Sabha directly influences village development.
- Visit the Gram Panchayat Office: If you have a specific issue or need information, visit the Gram Panchayat office during working hours. The Gram Sevak and Sarpanch should be accessible.
- Submit Formal Applications/Petitions: For significant issues, write a formal application addressed to the Sarpanch and Gram Sevak, detailing your concern and desired action. Keep a copy.
- Utilize Right to Information (RTI): If information is not readily available or if you suspect irregularities, the RTI Act is a powerful tool to seek details on Gram Panchayat finances, scheme implementation, or public works.
- Form Community Groups: Collaborate with like-minded villagers to form a collective voice for specific issues (e.g., a farmers’ group for irrigation issues, a women’s group for sanitation).
- Provide Constructive Feedback: Don’t just complain. If you see a problem, try to offer potential solutions or volunteer your time and skills.
- Support Development Initiatives: When the Sarpanch proposes or implements a positive development project, support it through your participation, volunteerism, or by simply spreading positive word.
- Know the Gram Sevak’s Role: The Gram Sevak is the administrative secretary of the Gram Panchayat and works closely with the Sarpanch. They are also a key point of contact for information and services.
- Leverage Digital Platforms (where available): While not as widespread as in urban areas, some Gram Panchayats might use WhatsApp groups or basic websites for communication. Use these channels respectfully and constructively.
Your active involvement ensures that the Sarpanch Responsibilities are not just theoretical mandates but are translated into tangible improvements in your village.
Conclusion: The Sarpanch – A Catalyst for Change
The role of the Sarpanch is arguably one of the most challenging yet rewarding positions in India’s democratic framework. Charged with a wide array of Sarpanch Responsibilities, from maintaining village records to driving large-scale infrastructure projects, they are the frontline leaders of rural development. In Sangli district, where agriculture, local industries, and community traditions intertwine, the Sarpanch stands as a critical catalyst for progress.
Their success is intertwined with the active participation and vigilance of the villagers they serve. By understanding their duties, supporting their efforts, and holding them accountable through democratic processes like the Gram Sabha, every citizen can contribute to building stronger, more vibrant, and self-reliant villages in Sangli. The future of rural Maharashtra rests significantly on the shoulders of these local leaders, and it is our collective duty to empower and engage with them for sustained growth and well-being.
📞 Contact for PR & Advertising in Satara, Sangli & Kolhapur
Want your story featured on Google, YouTube, Instagram, and our portals?
Reach out today for our PR packages tailored for:
- 🎥 Video shoots
- 📄 Blog + SEO combo
- 📱 Reels & WhatsApp creatives
- 🎙️ Audio podcast + social bundle
🔗 Contact Details:
📧 Email: rohitmorebiz@gmail.com
📞 Call / WhatsApp: +91 9659291592
🌐 Website: https://sanglidistrict.in/advertise-with-us/
Read More : https://sanglidistrict.in/category/news
Read this : https://kolhapurdistrict.in/
Rad This : https://sataradistrict.in/
Sarpanch Responsibilities, Sarpanch Responsibilities, Sarpanch Responsibilities, Sarpanch Responsibilities, Sarpanch Responsibilities, Sarpanch Responsibilities, Sarpanch Responsibilities, Sarpanch Responsibilities, Sarpanch Responsibilities, Sarpanch Responsibilities, Sarpanch Responsibilities, Sarpanch Responsibilities
- Introduction: The Foundation of Village Progress
- I. The Constitutional Mandate: Why Sarpanch Responsibilities are Crucial
- II. Core Administrative and Executive Sarpanch Responsibilities
- III. Development-Oriented Sarpanch Responsibilities
- IV. The Sarpanch and the Gram Sabha: A Symbiotic Relationship
- V. Challenges in Fulfilling Sarpanch Responsibilities
- VI. The Sarpanch’s Role in Specific Schemes (Illustrative for Sangli)
- VII. Engaging with Your Sarpanch: Empowering Rural Sangli
- Conclusion: The Sarpanch – A Catalyst for Change
- 📞 Contact for PR & Advertising in Satara, Sangli & Kolhapur


